From RimWorld to the Real World: How Skills and Passion Drive Organizational Success

In today’s fast-paced world, companies and their requirements evolve every day. Those that fail to adapt inevitably fall behind and leave the market. One of the most important KPIs, as highlighted in Jim Collins’ book Good To Great, is the percentage of key seats on the “bus” that are occupied by the right people for those roles.
To help you achieve this critical goal, I have an interesting perspective for you to consider.
🌍 RimWorld Deconstruction
In the game RimWorld, you act as the "invisible hand" guiding a colony of unique individuals, each with their own skills and passions.
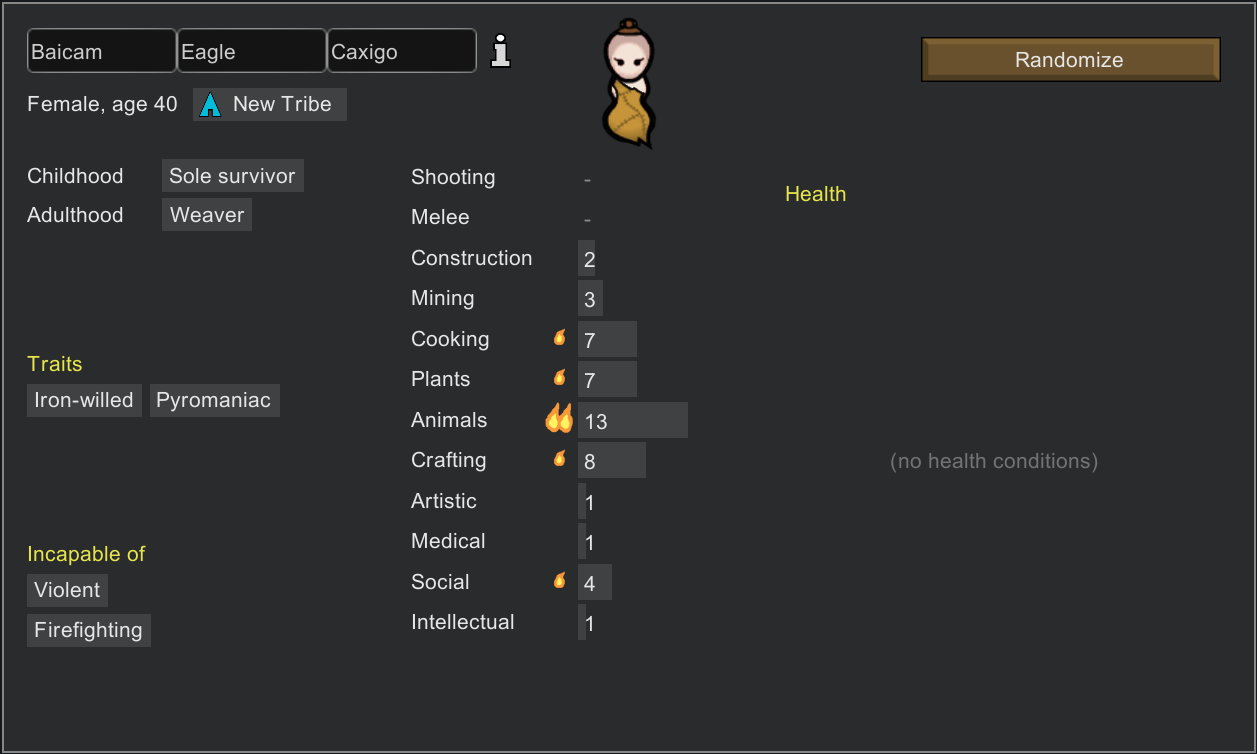
In RimWorld, certain skills are essential for your colony’s survival. For example:
- Shooting: The ability to use ranged weapons effectively in combat or hunting.
- Cooking: The skill to prepare quality, tasty food for the colony.
- Medical: Proficiency in healing injuries and performing surgeries.
Each skill is measured numerically, and the higher the number, the better the colonist is at it. A skill level of 1–4 indicates basic, often unreliable proficiency, while 8+ reflects a confident and competent specialist.
However, not every colonist can do every task. For example, a colonist without any skill in Shooting or Melee will avoid combat altogether, making them unsuitable for fights or hunting. Meanwhile, a colonist with 1–4 in Shooting will rarely hit their target, while one with 10+ will land most of their shots with ease. The more they practice, the more their skills grow—meaning consistent work leads to better performance over time.
The 🔥 Passion System
The most intriguing part of the skill system is the passion level, represented by 🔥 symbols next to a skill. Passion determines how quickly a colonist improves at a particular task and how much they enjoy doing it. In the long term, it’s often better to choose a colonist with low skill but high passion over one with moderate skill and no passion—because the passionate colonist will learn and grow much faster.
Passion levels work as follows:
- No Passion: The colonist gains experience at a standard rate and may view the task as mundane.
- Single Fire 🔥 (Minor Passion): The colonist gains experience 1.5x faster and enjoys working on this skill.
- Double Fire 🔥🔥 (Major Passion): The colonist learns 3x faster—this skill might even feel like their life’s purpose.
For example, a colonist with Double Fire 🔥🔥 in Cooking but a low initial skill will eventually become a master chef faster than someone with moderate skill but no passion.
Your ultimate goal in RimWorld is to build a thriving colony, but resources are limited, and the path to success is rarely straightforward. Matching each colonist's work with their highest skill and highest passion is one of the most effective strategies for long-term success. Passionate colonists improve rapidly, stay more engaged, and ultimately contribute more to the colony’s survival.
Interestingly, this approach is often undervalued in the corporate world. Projects require specific skills to succeed, and employees bring varying levels of expertise to the table. Some employees also have a natural passion for certain tasks, making them not only proficient but also highly motivated to improve. Just as in RimWorld
Aligning work with both skill and passion can lead to faster learning, better outcomes, and greater satisfaction
an approach that’s as valuable in business as it is in a survival game.
⭐ Skills
To adopt this approach, we can break down the work we do into specific skills that enable us to accomplish tasks effectively.
A skill is a defined area of competence that allows a person to perform tasks or solve problems in a professional or personal setting. Skills are:
- Actionable: They translate into tangible, real-world capabilities.
- Developable: With practice and effort, skills can improve and evolve.
- Applicable: Skills have a clear purpose and function in achieving goals.
For example, let’s say you want to deliver an engaging presentation to an audience. The Core Skill here would be Public Speaking. This skill can be developed by refining your communication style, learning effective delivery techniques, and using tools to create impactful visuals. While Public Speaking could be broken down into more specific Micro Skills—like voice modulation, slide design, or handling Q&A—focusing too much on these smaller components might become overwhelming and distract from the overall goal.
Skills can vary in scope:
- Core Skills: Broad, fundamental abilities like public speaking, problem-solving, or teamwork. These have a significant impact on the quality and success of the work.
- Micro Skills: Narrower, more specific abilities like managing tone, using presentation software, or structuring bullet points. These are useful but often have limited growth potential.
A good starting point is to define a skill as a distinct type of work activity you need to perform. Then, if necessary, break it down into Sub-Skills to refine your approach further.
Skills are the foundation of capability. They determine what a person can achieve and offer a virtually unlimited growth potential depending on their adaptability and complexity. Focusing on identifying and nurturing Core Skills—those with the highest impact and growth opportunities — is crucial for both personal and professional development.
🔥 Passion
In RimWorld, passion is represented by 🔥 symbols next to a colonist’s skills, showing how quickly they improve and how much they enjoy certain activities. Similarly, in the real world, passion acts as an XP multiplier—an accelerant that not only enhances the quality of work but also reduces burnout, boosts job satisfaction, and fosters a sense of ownership over the work being done.
Passion — is an intense enthusiasm or strong drive for something. It’s the energy and motivation that compels individuals to dedicate themselves wholeheartedly to pursuits they find meaningful or fulfilling. Passion arises when people engage in activities they love, are naturally drawn to, or find deeply significant.
Key Characteristics of Passion:
- Intrinsic Motivation: Passionate individuals engage in activities because they genuinely enjoy them, finding personal fulfillment rather than relying solely on external rewards like money or recognition.
- Flow State: Passion leads to a “flow state,” where individuals become fully immersed in their work, losing track of time and achieving heightened focus and creativity.
- Persistence and Energy: Passion drives determination and resilience, enabling people to overcome challenges while radiating enthusiasm that inspires others.
The Impact of Passion in the Workplace
Just like in RimWorld, where colonists with high passion for a skill grow faster and stay happier, passion in the workplace leads to transformative results when aligned with roles and responsibilities. By identifying and leveraging employees’ passions, organizations can achieve:
- Higher Engagement: Employees are more focused, motivated, and effective when working on tasks they’re passionate about.
- Better Retention: Passionate employees feel a stronger sense of fulfillment and purpose, reducing turnover.
- Increased Innovation: Passion sparks creativity, encouraging new ideas and out-of-the-box thinking.
Passion isn’t just a personal trait. It’s a powerful tool for growth, performance, and satisfaction. By aligning employees’ passions with their work, leaders can cultivate a more dynamic, innovative, and resilient team—just like optimizing your colony in RimWorld.
👔 Roles
Employees are not defined by a single skill—they bring a Skill Set and Passions to their work. Let’s break these concepts down:
✨ Skill Set: A collection of skills an individual is confident in using effectively.
While skills are common and transferable, roles are context-specific and variable.
- ⭐ Skills: The same skill (e.g., UX prototyping) can apply to multiple roles, such as UX Designer, Game Designer, or UI Developer.
- 👔 Roles: Job titles like "UI Designer" or "Game Designer" vary between companies, but the underlying skills required for these roles are often consistent.
For example, a Software Developer at one company might focus mainly on front-end tasks, while at another, they could also handle back-end or DevOps responsibilities. However, foundational skills like coding best practices, debugging, and version control remain universally relevant.
Why Skills Matter More Than Roles
- Skills Are Standardized:Skills are easier to measure, train, and certify than roles. Certifications like Agile, Unity, or SQL validate specific skills, not job titles.
- Evolving Roles, Timeless Skills:As industries evolve, new roles emerge, but foundational skills (e.g., programming, data analysis) remain relevant and expand.
Example: The rise of AI in games has created roles like AI Narrative Designer, but the core skills (narrative writing, AI scripting) are long-standing.
For Individuals
- Clear Development Path: Skills provide a roadmap for career growth even as roles change.
- Example: Mastering game economy balancing can prepare someone for roles like Game Designer, Monetization Specialist, or even Product Analyst.
- Career Flexibility: Transferable skills allow individuals to move between roles or even industries, ensuring long-term adaptability.
For Companies
- Better Hiring Practices:You don’t have to rename every position to a list of skills, but placing greater emphasis on specific competencies rather than job titles can yield more accurate hires.
- Efficient Training:Upskilling employees through targeted workshops (e.g., monetization strategies) ensures their skills align with company goals.
- Custom Role Design:Companies can design roles to fit their specific needs by combining skill sets.
From RimWorld to the Real World
Types of Specialists
As you gather your team, you’ll encounter two main types of specialists:
- Narrow Specialists — Highly skilled in their niche, but struggle to adapt to tasks outside their expertise.
- General Specialists (Generalists) — Versatile and adaptable, but may lack the deep expertise needed for specialized tasks.
And 🔥Passion fundamentally transforms how specialists contribute to the team:

By balancing skills, roles, and passion within your team, you can build not just a functional group but a thriving, dynamic force capable of creating something extraordinary!
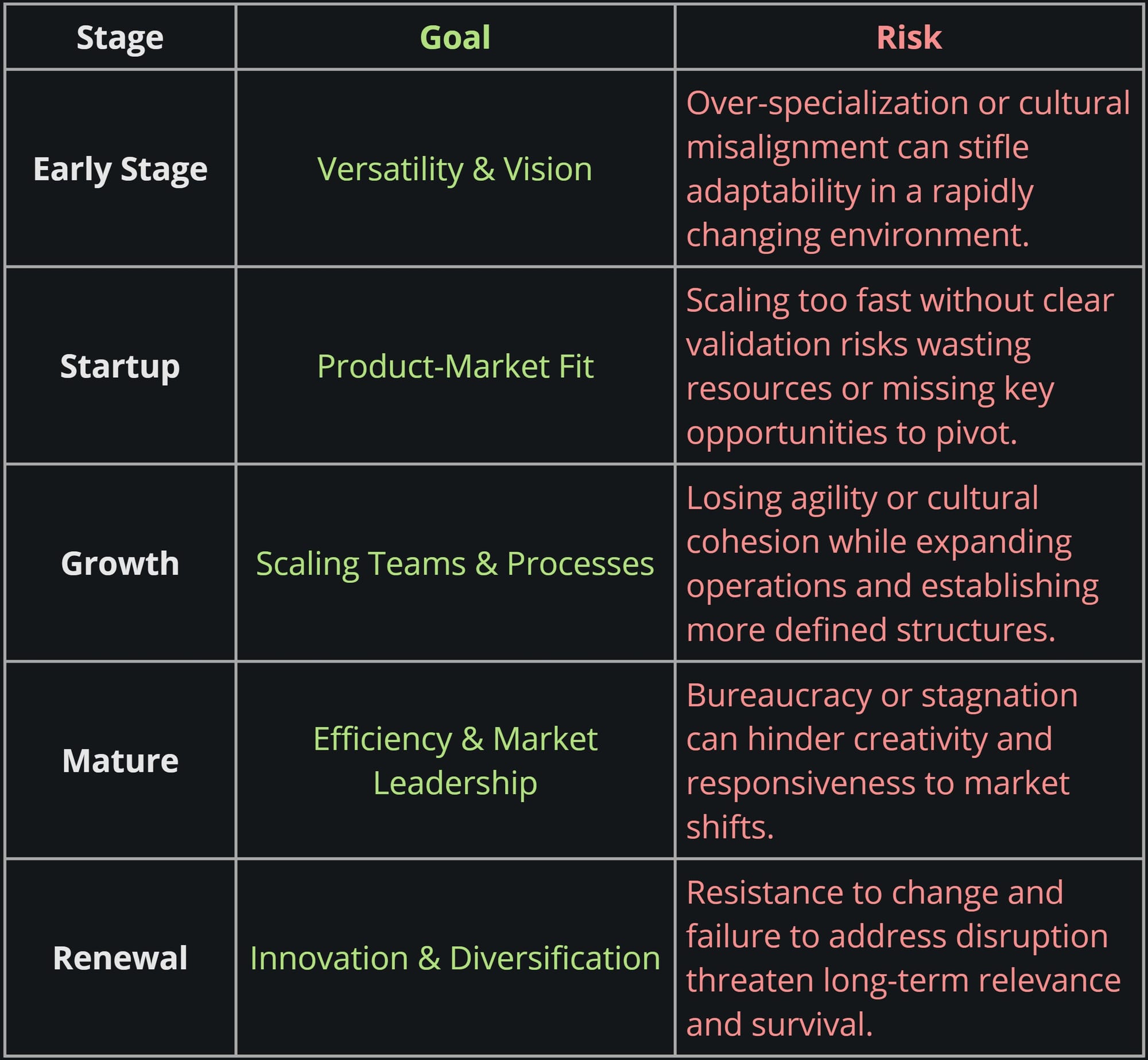
Roles in Company Growth Stages
There are 5 main company stages with unique goals and risks:
Laying the Foundation
- Aligning skills, roles, and passions with the organization’s goals is key to building a strong team.
- As a company grows, its needs and challenges change, requiring a shifting balance between generalists and specialists.
Early Stages
- Unpredictable Environment: Early-stage companies need rapid adaptation to survive.
- Value of Generalists: Individuals who can handle multiple responsibilities and pivot quickly excel during this phase.
Growth, Maturity, and Beyond
- Focus on Specialization: In the growth and maturity phases, narrow specialists drive efficiency and high-quality outcomes.
- Renewal or Diversification: As markets evolve, reintroducing generalists fosters collaboration and innovation, while specialists remain crucial for technical expertise.
There are few Real-World Methodologies for Managing Skills and Passion
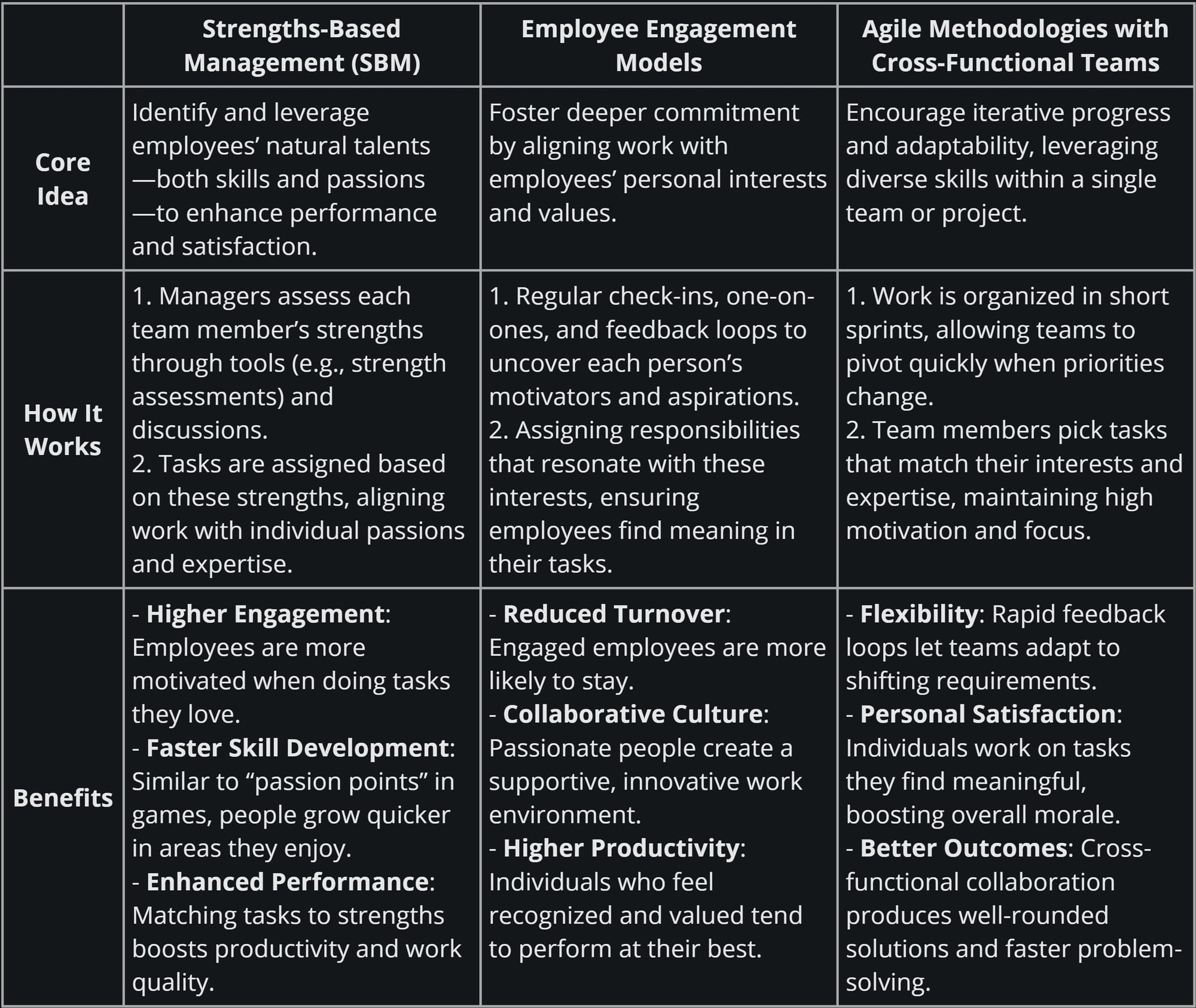
Building a Passion-Centric Talent Management Approach
To fully adopt a talent management system that emphasizes passion and engagement, you can combine the strengths of these approaches into a cohesive framework:
1. 🔎 Map Core Skills and Roles
List tasks, identify required skills, and note each team member’s strengths in a simple chart.
2. 👥 Discover Strengths & Passions
Conduct one-on-ones and group discussions to uncover personal interests and motivations.
3. 📈 Provide Growth Opportunities
Offer small pilot projects, peer mentoring, or targeted learning aligned with individual aspirations.
4. 🔄 Foster Flexibility
Allow brief task swaps or slight role adjustments to spark creativity and maintain engagement.
5. 📣 Encourage Open Feedback
Schedule regular check-ins, praise publicly, and keep communication channels open for suggestions.
6. 🏆 Recognize & Reward
Celebrate achievements tied to passion, highlight impact, and offer simple perks or acknowledgments.
Challenges of a Skills-and-Roles Approach
While the skills-and-roles model has its advantages, there are notable challenges:
- Honesty in Passion: Unlike RimWorld, where characters are honest about their passion levels, people in real life might not be. Passion can be difficult to gauge, and misrepresentation is always a risk.
- (Fun fact: A U.S. general once joked about StarCraft 2 workers being shockingly consistent because they worked even when no one was watching. Real life, of course, is different!)
- System Maintenance:
- Designing and maintaining a system to track skills and levels is labor-intensive. Someone must define each skill, its levels, and how they are measured.
- Achieving alignment is challenging—different people may disagree on the meaning or value of specific skills and their levels.
Conclusion
Adopting a talent management approach that prioritizes passion and engagement has the power to unlock exceptional levels of productivity and commitment within a team. By focusing on aligning individuals’ skills and passions with their roles, organizations can create an environment where employees thrive, feel valued, and deliver their best work.
For individuals, identifying and sharing your skills and passions is essential for finding fulfilling opportunities or enhancing your current role. When you engage in tasks that resonate with your strengths and interests, it not only reduces burnout but also reignites enthusiasm and fosters personal growth.
For organizations, understanding and aligning employees’ passions with their responsibilities can be transformative. Hiring with a focus on passions and skills, rather than just qualifications, helps build a team that is motivated, innovative, and deeply engaged. This alignment creates a win-win scenario, where both individuals and companies benefit from shared success and meaningful collaboration.
Passion-driven initiatives open doors to innovation and inspire a stronger sense of ownership and responsibility among employees. Ultimately, the most effective way to build a thriving team is to place the right people in the right roles, ensuring their passions align with organizational goals. This approach not only boosts performance but also lays the foundation for a dynamic, successful, and enduring workplace culture.

